China's Tech Takeover Threat
China's tech ambitions are reshaping the global landscape, with its aggressive subsidies and strategic focus on AI and EVs threatening to upend US dominance.

As the tech rivalry between the United States and China intensifies, concerns are mounting that China's aggressive subsidies and strategic focus on artificial intelligence and electric vehicles could reshape the global tech landscape, much like how Chinese manufacturing transformed the industrial sector. With Beijing pouring billions into AI research and EV development, some worry that Silicon Valley's dominance may be challenged in ways eerily reminiscent of the decline of American manufacturing.
China's Trade Surplus Leaders
China has become the largest trading partner for numerous countries worldwide, reflecting its growing economic influence.
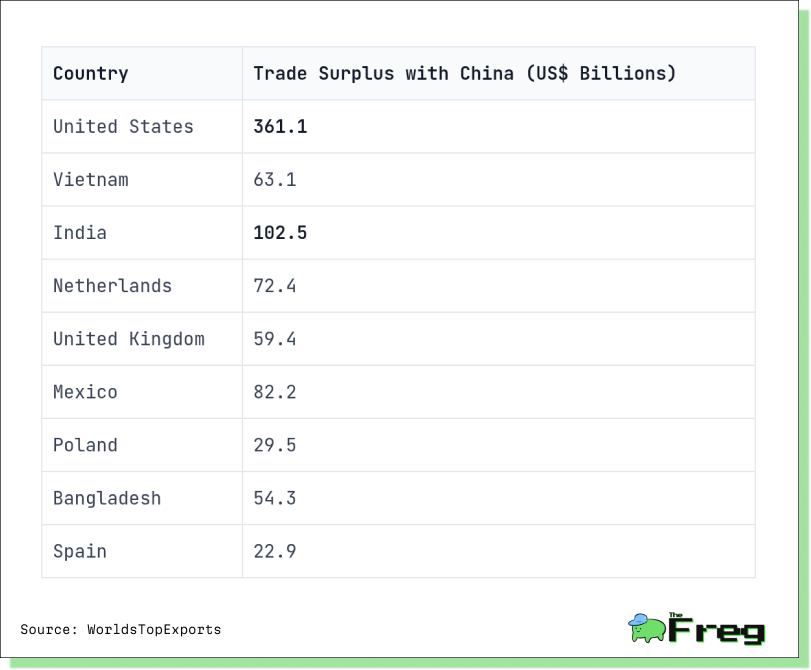
China's significant trade surpluses with various countries and territories in 2024. The United States tops the list with a massive $361.1 billion trade deficit with China. Notably, China maintains substantial surpluses with both developed economies like the Netherlands and the UK, as well as emerging markets such as Vietnam and India. These figures underscore China's position as a global export powerhouse and highlight the trade imbalances that have fueled ongoing economic tensions, particularly with the United States.
China's AI Subsidy Strategy
China's AI subsidy strategy is a multifaceted approach aimed at propelling the nation to the forefront of global AI innovation. The government employs various financial mechanisms to support domestic AI firms, including:
- Government guidance funds: Public-private investment vehicles that have injected billions into AI startups, with over 2,100 funds targeting a staggering $1.86 trillion in investments.
- Computing vouchers: Provincial governments offer subsidies worth up to $300,000 per company to offset rising cloud computing costs.
- Direct grants and competitions: National programs like the AI Industry Alliance distribute cash prizes and research subsidies to promising AI startups.
- Infrastructure investments: Beijing has poured over $6 billion into constructing computing hubs in western provinces to address the shortage of advanced AI chips.
This aggressive funding strategy, combined with China's focus on developing more efficient and cost-effective AI technologies, positions the country to potentially dominate AI adoption in emerging markets frustrated by U.S. restrictions. As a result, China is rapidly narrowing the gap with U.S. competitors, challenging America's AI leadership on the global stage.
AI Commoditization by China
China's aggressive push into artificial intelligence (AI) is raising concerns about the potential commoditization of AI technologies. Recent developments suggest that Chinese companies are making significant strides in offering high-performance AI models at drastically reduced prices compared to their Western counterparts.
Baidu's release of ERNIE X1, a reasoning model that claims to match DeepSeek R1's performance at nearly half the price, exemplifies this trend. With input and output token costs at $0.28 and $1.10 per million respectively, compared to
GPT-4.5's $75 and $150, the price gap is staggering. This aggressive pricing strategy, coupled with China's vast data resources and government support, could accelerate AI adoption globally, particularly in emerging markets. However, questions remain about the sustainability of such pricing and whether it reflects genuine innovation or strategic subsidies aimed at undercutting U.S. competitors.
Impact of EV Incentives
China's approach to EV manufacturer incentives has been more comprehensive and long-term focused compared to the United States. Since 2009, the Chinese government has invested heavily in the EV industry, providing an estimated
$231 billion in subsidies from 2009 to 2023. These incentives included direct subsidies to manufacturers, tax exemptions, and support for research and development.
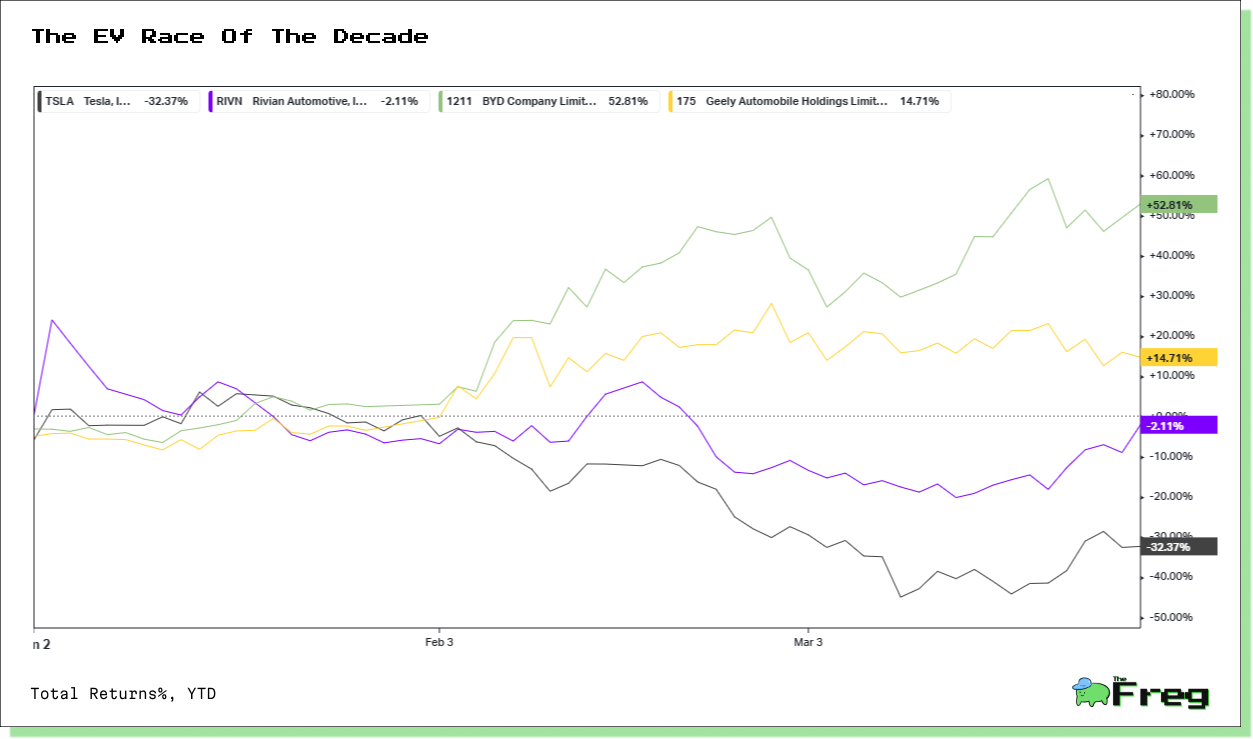
In contrast, the U.S. has taken a less aggressive approach, focusing more on consumer-side incentives. While the U.S. offers tax credits of up to $7,500 per vehicle, these are subject to strict eligibility criteria and are set to phase out. China's strategy of supporting the entire EV supply chain, particularly battery production, has given its manufacturers a significant advantage. As a result, Chinese EV makers are now 30% faster in developing and releasing new car models compared to their American counterparts, highlighting the impact of China's sustained industrial policy support on innovation and competitiveness in the global EV market.
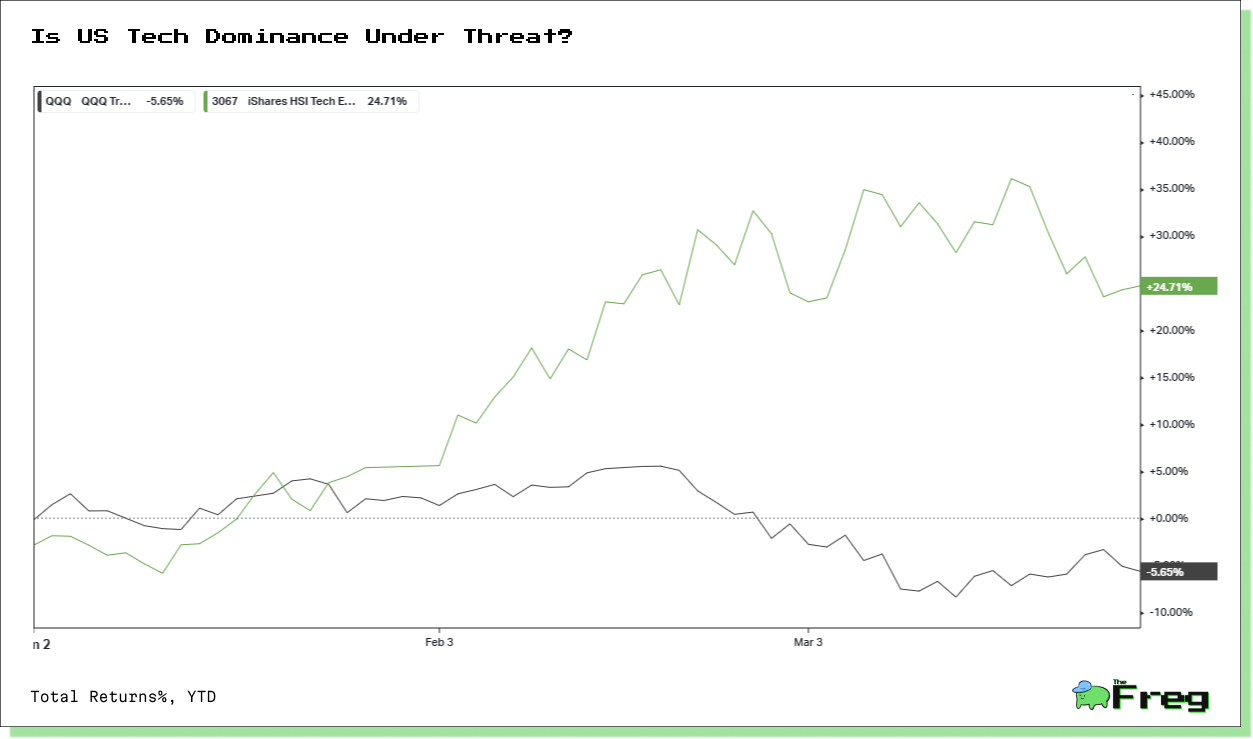
The tech rivalry between China and the US is intensifying at breakneck speed. China is funneling substantial subsidies into its industries, aiming to commoditize artificial intelligence and seize dominance in the electric vehicle market. Meanwhile, the US is racing to protect its competitive edge, setting the stage for a future where AI and EVs could become as ubiquitous as smartphones.
This isn’t just another chapter in global competition; it’s a potential turning point. Should China succeed in reshaping these markets, the resulting transformation could eclipse the impact of past manufacturing shifts. The next decade promises high-stakes drama as these tech giants vie for supremacy on the global stage.