Japan's Export Growth in March 2025: Strength in Innovation, Shadows of Tariffs
Japan’s exports rose for a sixth straight month in March 2025, but rising U.S. tariffs and global headwinds pose risks to sustained growth.
Japan’s export engine continued to hum in March 2025, expanding for the sixth consecutive month with a year-on-year increase of 3.9%. The steady momentum, however, comes amid growing unease about U.S. tariffs that are already beginning to shape strategies at boardrooms across Tokyo.
A Mixed Picture: Growth, but Below Expectations
The 3.9% export growth, while positive, came in below the 4.5% consensus forecast. Most of this growth was powered by transport equipment, with motor vehicles rising 7.2% and cars up 6.7%. This came even as Japanese exporters braced for tariffs from the United States—a 25% automobile tariff took effect on April 3rd, and steel/aluminum duties were enacted on March 12th.
Policy Reverberations and Strategic Shifts
Economists are already ringing alarm bells. The Trump administration’s tariff measures are projected to cut Japan’s economic growth by 0.6 percentage points in the fiscal year ending March 2026. The automotive sector is bearing the brunt, with major players like Toyota, Honda, Nissan, and Mazda facing combined annual losses of up to ¥1.6 trillion (approximately C$15.3 billion).
To mitigate the blow, companies are pivoting quickly. Nissan will slash Rogue SUV production at its Kyushu plant by 13,000 units. Honda is exploring a deeper supply chain partnership with Toyota to tap hybrid battery supplies from North Carolina. In response, Tokyo has formed a government committee to tackle what officials describe as a "national crisis," and domestic stimulus—including potential cash handouts—is under consideration.
Automotive Sector Defies Gravity—For Now
Despite uncertainty, Japan’s automotive sector delivered strong numbers in March. Total vehicle sales rose 10.7% to 499,745 units. Larger-engine vehicles (above 660cc) increased by 8.8% to 329,918 units. These figures reinforce the sector's resilience, even as its future profitability becomes more clouded.
However, with tariff repercussions on the horizon, the pain may soon outweigh the gain. Goldman Sachs projects significant profit slashes for automakers—Mazda and Nissan could see earnings fall by 59% and 56% respectively. Small suppliers are particularly vulnerable if production shifts offshore.
Electronics and Semiconductors: Resilient Yet Uneven
The electronics sector held its ground with a 1.4% rise in March. Semiconductor shipments, a linchpin of Japan's tech economy, rose 4.2%, buoyed by robust demand from Asia. This growth came even as the export price index for electronic products dipped by 0.87% from February.
Japan’s electronics exports now constitute roughly 17% of total shipments. Key markets like Taiwan (+19.5%), Hong Kong (+19.7%), and South Korea (+11.5%) absorbed much of this output, even as exports to China fell 4.8%—a reflection of shifting supply chain priorities amid rising geopolitical tensions.
Sectoral Highlights: Precision Technology Leads
Several high-value export categories posted notable gains. Scientific and optical instruments led with 15.4% year-on-year growth, underscoring Japan’s strength in precision manufacturing. The automotive sector remained dominant, driven by innovation in hybrid vehicles. Machinery, chemicals, and semiconductors also expanded.
The following table summarizes the top 5 export categories:
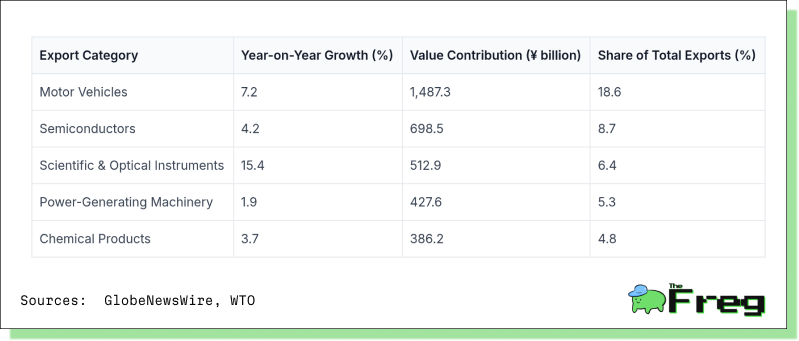
These five sectors collectively account for roughly 44% of Japan’s total exports, offering a snapshot of the country’s economic lifelines.
Category-Wise Export Growth Overview
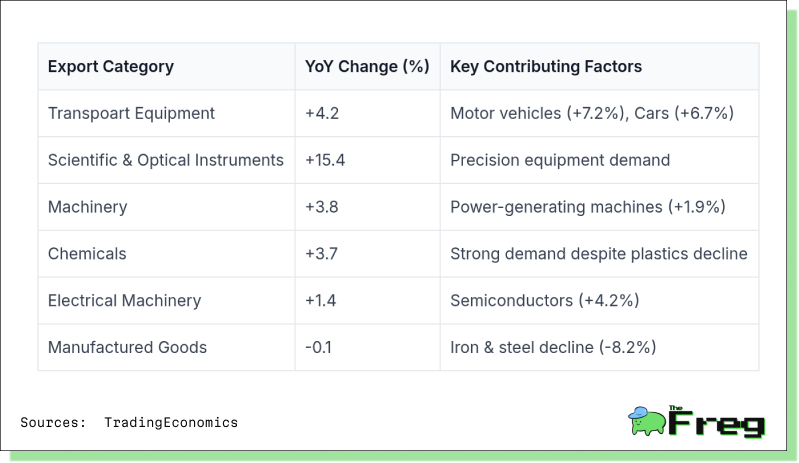
This breakdown highlights Japan’s comparative advantage in high-value sectors even as traditional manufactured goods face headwinds.
Where the Goods Go: Export Destinations
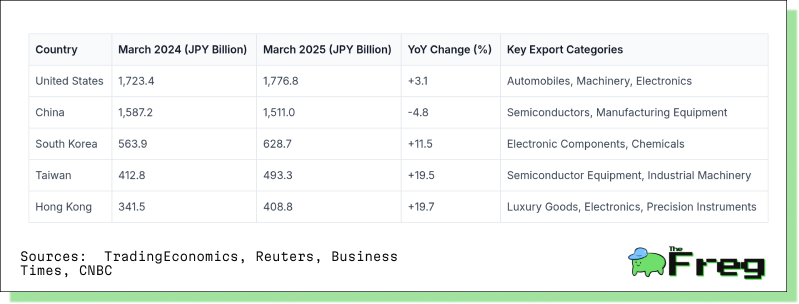
March’s export destination data reveals a reconfiguration of trade flows. While the United States remained Japan’s largest customer with 3.1% growth, exports to China slumped 4.8%, echoing ongoing trade frictions.
However, other Asian markets outshone: exports to Hong Kong surged 19.7%, Taiwan 19.5%, and South Korea 11.5%. This suggests Japan is actively rerouting trade within Asia to hedge against U.S.-China volatility. ASEAN nations, led by Singapore and Thailand, also contributed to this regional pivot.
Exports to Europe declined by 1.1%, highlighting economic softness in the EU and offering a cautionary note on diversification efforts.
Country-Wise Export Value Comparison
Corporate Leaders in Export Performance
On the corporate front, Toyota Kirloskar Motor (TKM) delivered a stellar fiscal year, with 337,148 units sold—a 28% year-on-year increase. Exports jumped 59%, underscoring India’s role as a vital production hub for the brand.
Elsewhere, Hitachi inked a major transmission systems deal with BHEL in India to support renewable energy development. Sony, battling softer PS5 sales, doubled down on its audio equipment line, recording 2x annual growth in India for its ULT Power Sound brand.
Navigating the Crosswinds
Japan’s export story in March 2025 is one of cautious optimism. The numbers show sustained demand and a clear tilt toward high-tech products, but clouds are gathering. Tariffs from the U.S., geopolitical uncertainty, and global economic softness all pose risks to Japan’s trade-dependent economy.
With a trade-to-GDP ratio of 40%, Japan must tread carefully. How the country adapts—particularly in the automotive sector—will determine whether it can preserve export momentum or see it wane under external pressures.
For now, resilience is the keyword. But flexibility and foresight will decide the future.






