Rev or Ruin? The Auto Industry Braces for Trump’s Tariff Hike
President Trump's 25% tariff on imported vehicles threatens to disrupt U.S. automakers, driving up production costs and car prices.

President Donald Trump's announcement of a 25% tariff on imported vehicles and auto parts has sent shockwaves through the global automotive industry, with U.S. automakers facing potential disruptions to their supply chains and increased production costs. This move has rattled stock markets and raised concerns about higher vehicle prices for consumers, setting the stage for a significant reshaping of the automotive landscape in North America.
A Supply Chain in Crisis
The tariffs have sent trucking rates soaring as companies rush to move parts ahead of the policy shift. Suppliers, already under pressure, face the harshest impact, with costs piling up and production timelines thrown into chaos. Automakers, meanwhile, are scrambling to find alternatives, but potential solutions come with trade-offs:
- Restructuring supply chains could add thousands to production costs, increasing car prices for consumers.
- Relocating manufacturing could drive up labor costs and worsen existing workforce shortages.
- Production delays and rising expenses threaten to slow output and impact bottom lines.
Market Fallout: How Automakers Reacted
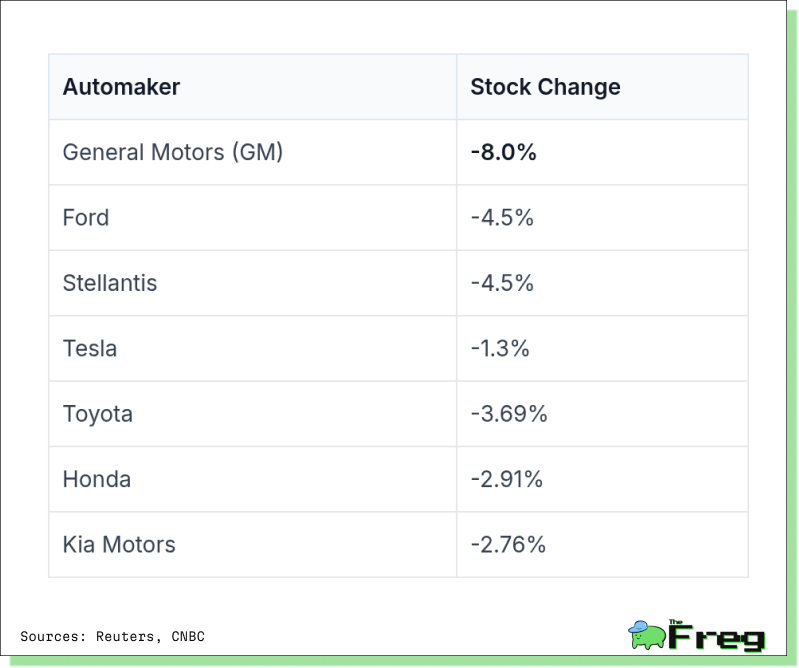
The stock market didn’t take the tariff news lightly. General Motors’ stock tumbled 8% in after-hours trading, while Ford and Stellantis fell about 4.5%. Even Tesla, despite its domestic production edge, dipped 1.3%, reflecting broad investor uncertainty.
Foreign automakers, especially those with production facilities outside the U.S., were hit hard. Toyota and Honda saw declines of nearly 3.7% and 2.9%, while South Korean manufacturer Kia also dropped 2.76%.
Automaker Stock Reaction to 25% Tariffs:
Stock Market Turmoil: The Bigger Picture
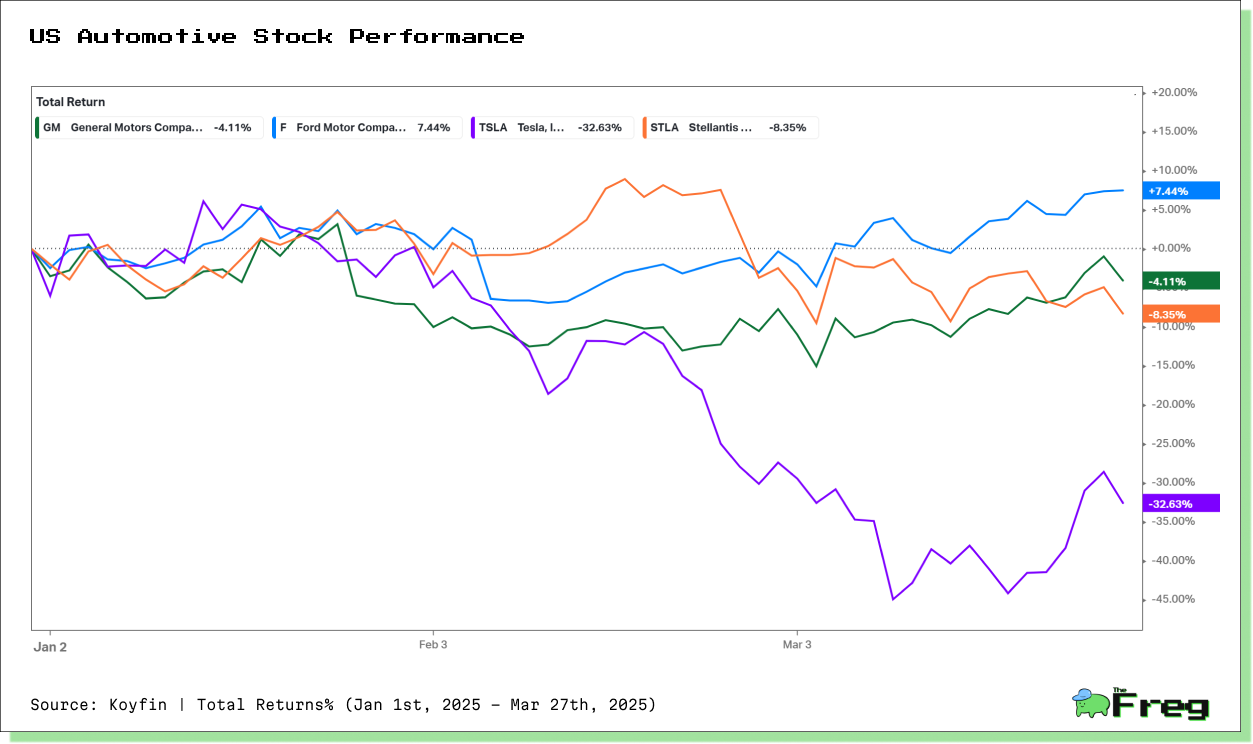
Before the tariff announcement, U.S. automakers were already struggling with trade uncertainties. The S&P 500 index had dropped over 4% in the month leading up to the news, marking its worst monthly performance in nearly a year. The tariff shock only deepened the downturn, reflecting investor fears of supply chain disruptions and rising costs.
Even Tesla, with its largely domestic production, saw its stock dip, underscoring concerns about the ripple effects on electric vehicle supply chains. Across the board, automakers are bracing for profitability challenges, with global supply chains now under intense scrutiny.
Price Surge: What Consumers Can Expect
Car buyers are in for sticker shock. Analysts predict price hikes of up to
$12,200 per vehicle, with North American-assembled models rising between $4,000 and $10,000. Electric vehicles, which depend heavily on imported parts, could see the steepest increases.
Even without the full 25% tariff, lingering trade barriers could add $2,000+ to car prices, pushing the average new vehicle—already near $49,000—further out of reach for many middle-class buyers. As costs rise, demand could plummet, potentially slashing U.S. factory production by 30% per week and triggering job losses across the auto sector.
Shifting Gears: The Road Ahead
As the dust settles, the long-term effects of these tariffs remain uncertain. Automakers will have to decide whether to absorb costs, pass them on to consumers, or restructure their supply chains altogether. One thing’s for sure—the North American auto industry is at a crossroads, and the ride ahead looks anything but smooth.